



Find all of your laboratory and workplace safety supplies at Safety Emporium!
 Polymer |
 Glossary Index |
 Pressure Units |
| MSDS Topics |
Free Sites | FAQ's | Regulations | Glossary | Software | Suppliers |
| Books | Forum | Poll | Fun stuff | Quiz | Store | |
| Understand your MSDS with the MS-Demystifier | Search ALL our MSDS info | |||||
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) includes all clothing and other work accessories designed to create a barrier against workplace hazards. Examples include safety goggles, blast shields, face shields, hard hats, hearing protectors, gloves, respirators, aprons, and work boots.
PPE should not be used as a substitute for engineering, work practice, and/or administrative controls to prevent exposure to hazardous chemicals. For example, a respirator is not meant to be worn by an assembly line worker during his/her entire work shift; other methods such as a ventilation system or replacement of hazardous substances/processes should be utilized. However, PPE can work in conjunction with such preventative measures or when such controls are not possible.
Also keep in mind that PPE protects only the user - it does nothing to remove the hazard from the workplace. For example, a respirator may help protect the wearer from toxic fumes, but does nothing to protect others in the vicinity.
In that context, in March 2021 the US EPA announced that if a review of a new chemical under TSCA found that the substance poses a potential unreasonable risk to workers, it would consider the possibility that necessary safeguards such PPE might not be provided as a "reasonably foreseen" condition of use, and mandate additional actions as appropriate.
Some of the most important OSHA PPE regulations for those who work with chemicals include.

Make your PPE readily available with safety dispensers from Safety Emporium.
Additional standards cover items such as hearing protection, foot protection etc. Many of OSHA's other standards require the use of PPE.
With few exceptions, such as prescription safety glasses and safety-toe boots, OSHA requires employers to pay for personal protective equipment when it is used to comply with OSHA standards. See Final Rule 72:64341-64430 dated Nov 15, 2007.

Get your PPE such as made in USA NIOSH-approved N95 masks from Safety Emporium.
NOTE: We may collect a share of sales or other compensation from the links in the following list:
OSHA requires that Section 8 (exposure controls/personal protection) of Safety Data Sheets list information about appropriate PPE for each substance. Pay careful attention to these as not all PPE is appropriate at all times. For example, certain gloves will do little to protect you from certain chemicals; see the glove selection guide links below for more information. Likewise, an organic vapor cartridge respirator will be useless at protecting you from an atmosphere deficient in oxygen.
In addition to using PPE appropriately, remember that every piece of PPE has limitations. For example, gloves may develop small holes and respirator cartridges generally do not indicate when they need replacement. Even appropriate PPE does not provide a 100% guarantee of safety.
Remember, the preferred methods for reducing chemical exposure, in order of general effectiveness, are illustrated in this diagram:
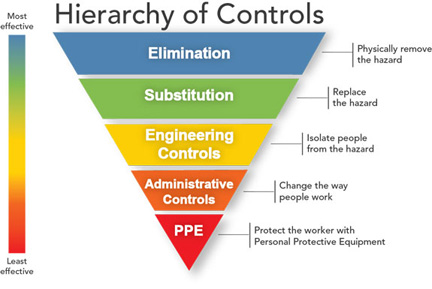
Specifically, these steps are:

Your employees can stay informed and comply with OSHA regulations with SDS information stations and compliance products from Safety Emporium.
Technical articles on glove testing:
See also: action level, administrative controls, engineering controls, HMIS, permissible exposure limit.
Additional definitions from Google and OneLook.
Entry last updated: Saturday, January 7, 2023. This page is copyright 2000-2025 by ILPI. Unauthorized duplication or posting on other web sites is expressly prohibited. Send suggestions, comments, and new entry desires (include the URL if applicable) to us by email.
Disclaimer: The information contained herein is believed to be true and accurate, however ILPI makes no guarantees concerning the veracity of any statement. Use of any information on this page is at the reader's own risk. ILPI strongly encourages the reader to consult the appropriate local, state and federal agencies concerning the matters discussed herein.