



Find all of your laboratory and workplace safety supplies at Safety Emporium!
 Ether |
 Glossary Index |
 Exothermic |
| MSDS Topics |
Free Sites | FAQ's | Regulations | Glossary | Software | Suppliers |
| Books | Forum | Poll | Fun stuff | Quiz | Store | |
| Understand your MSDS with the MS-Demystifier | Search ALL our MSDS info | |||||

Get your GHS-compliant labels and signs from Safety Emporium.
On Safety Data Sheets: An evaporation rate is the rate at which a material will vaporize (evaporate, change from liquid to vapor) compared to the rate of vaporization of a specific known material. This quantity is a ratio, therefore it is unitless.
General usage: The mass of material that evaporates from a surface per unit time (examples: 3 grams per square meter per hour, 1 inch per acre per month).
Evaporation rates generally have an inverse relationship to boiling points; i.e. the higher the boiling point, the lower the rate of evaporation. However, two substances with the same boiling point can have significantly different evaporation rates.
The general reference material for evaporation rates is n-butyl acetate (commonly abbreviated BuAc) which has the chemical structure shown below. Whenever a relative evaporation rate is given, the reference material must be stated.
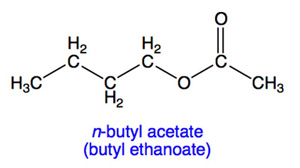
The relative evaporation rate of butyl acetate is 1.0. Other materials are then classified as:
We are not aware of a specific number for the absolute evaporation rate (i.e. in mass/time units) of butyl acetate. Presumably, such a number would depend on myriad variables such as temperature, atmospheric pressure, humidity, air flow, viscosity etc. The ASTM developed a standard test method, D3539-87(2004) Standard Test Methods for Evaporation Rates of Volatile Liquids by Shell Thin-Film Evaporometer, but it was withdrawn in 2015 without public explanation.
In the absence of evaporation rate data, you can roughly assess the volatility using the vapor pressure of the material. A number of models are available in the scientific literature; see Further Reading below for some examples.
If applicable and known, a substance's evaporation rate will appear in Section 9 (physical and chemical properties) of the Safety Data Sheet.
Evaporation rate can be useful in evaluating the health and fire hazards of a material. For example, a substance with a high evaporation rate will readily form a vapor which could be inhaled or explode.

Vent your flammable storage safety cabinets safely with Safe-T-Vent thermally-actuated dampers from Safety Emporium.
See also: alcohol, boiling point, vapor pressure, volatility.