 |
 Safety Emporium is a proud sponsor of this site. |
 |
Home Page --> Glassblowing Data and Tables
|
Glassblowing Data, Tables, and Resources
This is a collection of handy conversion tables and other technical data that a scientific glassblower will find useful. On this page you will find:
- Spherical Volumes including a calculator
- Cylindrical Volumes including a calculator
- Fractional Inches to Millimeter Conversions
- Temperature Conversions
- Pressure Conversions
- Glass Tubing Pressure Nomogram
- Physical Properties of Common Glasses
- Glass to Metal Sealing Combinations
- Vacuum Formed 0.500" OD Quartz Tubing
- Glass Frit Porosities
- Glass Properties and Technical Data Sources
- General and Miscellaneous Technical Resource
General Glassblowing Resources Page which covers books, organizations, tool suppliers, glass suppliers, descriptions of laborator glassware, and art glass links.
Spherical Volumes
This handy chart correlates the nominal volume (V) of a sphere in milliliters to the internal diameter in millimeters:
| V (ml) | 1 | 5 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 500 | 800 | 1,000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID (mm) | 12 | 21 | 27 | 36 | 46 | 57 | 62 | 66 | 72 | 78 | 83 | 87 | 91 | 98 | 115 | 124 |
The relationship between volume and radius/diameter is given by V = (4/3)πr3 where V is the volume, r is the radius of the sphere and π = 3.1415…. This JavaScript calculator gives a precise conversion between volume in mL and inner diameter in mm:
If you need them, we also have some unit conversion calculators for distance and volume.
Cylindrical Volumes
Glassblowers sometimes need to calculate the volume of a cylinder of a given length or diamter. This handy chart lists the height and ID required to give a volume of 1 mL. For example, by looking at the chart we can see that a cylinder of ID 42 mm has volume of 1 mL for every 0.72 mm of height.
| ID mm |
Height mm |
ID mm |
Height mm |
ID mm |
Height mm |
ID mm |
Height mm |
ID mm |
Height mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1274 | 21 | 2 | 41 | 0.760 | 61 | 0.340 | 81 | 0.194 |
| 2 | 318 | 22 | 2.630 | 42 | 0.720 | 62 | 0.330 | 82 | 0.190 |
| 3 | 141 | 23 | 2.450 | 43 | 0.690 | 63 | 0.320 | 83 | 0.185 |
| 4 | 79 | 24 | 2.210 | 44 | 0.658 | 64 | 0.310 | 84 | 0.180 |
| 5 | 51 | 25 | 2.030 | 45 | 0.630 | 65 | 0.300 | 85 | 0.176 |
| 6 | 35 | 26 | 1.880 | 46 | 0.600 | 66 | 0.292 | 86 | 0.172 |
| 7 | 26 | 27 | 1.740 | 47 | 0.580 | 67 | 0.283 | 87 | 0.168 |
| 8 | 20 | 28 | 1.620 | 48 | 0.550 | 68 | 0.275 | 88 | 0.164 |
| 9 | 15 | 29 | 1.510 | 49 | 0.530 | 69 | 0.267 | 89 | 0.160 |
| 10 | 12 | 30 | 1.410 | 50 | 0.510 | 70 | 0.260 | 90 | 0.157 |
| 11 | 10 | 31 | 1.320 | 51 | 0.490 | 71 | 0.252 | 91 | 0.154 |
| 12 | 8 | 32 | 1.240 | 52 | 0.470 | 72 | 0.245 | 92 | 0.150 |
| 13 | 7 | 33 | 1.170 | 53 | 0.450 | 73 | 0.239 | 93 | 0.147 |
| 14 | 6 | 34 | 1.100 | 54 | 0.437 | 74 | 0.232 | 94 | 0.144 |
| 15 | 5.660 | 35 | 1.040 | 55 | 0.420 | 75 | 0.226 | 95 | 0.141 |
| 16 | 5 | 36 | 0.982 | 56 | 0.406 | 76 | 0.220 | 96 | 0.138 |
| 17 | 4 | 37 | 0.930 | 57 | 0.392 | 77 | 0.215 | 97 | 0.135 |
| 18 | 3 | 38 | 0.880 | 58 | 0.378 | 78 | 0.209 | 98 | 0.133 |
| 19 | 3 | 39 | 0.837 | 59 | 0.366 | 79 | 0.204 | 99 | 0.130 |
| 20 | 3 | 40 | 0.790 | 60 | 0.356 | 80 | 0.199 | 100 | 0.127 |
The relationship between the height, radius/diameter and volume of a cylinder is given by V=hπr2 where V is the volume, h is the height, r is the radius (half the inner diameter) and π = 3.1415…. In the JavaScipt calculator below, you can enter any two of the three variables and it will determine the value of the third one for you.
If you need them, we also have some unit conversion calculators for distance and volume.
Fractional Inches to Millimeter Conversions
Glassblowers routinely use calipers to measure glassware, and some of these even read in both inches and millimeters. However, most calipers do not handle fractional measurements such as 11/16". This table is list of fractional measurements along with their decimal and millimeter equivalents that you may want to print and hang by your workbench. This table is great for woodworkers,too!
| Fraction (Inches) | Decimal (Inches) | Millimeters |
|---|---|---|
| 1/64 | 0.015625 | 0.396875 |
| 1/32 | .03125 | 0.7938 |
| 1/16 | 0.0625 | 1.5875 |
| 1/8 | 0.125 | 3.1750 |
| 3/16 | 0.1875 | 4.7625 |
| 1/4 | 0.250 | 6.3500 |
| 5/16 | 0.3125 | 7.9375 |
| 3/8 | 0.375 | 9.5250 |
| 7/16 | 0.4375 | 11.1125 |
| 1/2 | 0.500 | 12.7001 |
| 9/16 | 0.5625 | 14.2876 |
| 5/8 | 0.625 | 15.8751 |
| 11/16 | 0.6875 | 17.4625 |
| 3/4 | 0.750 | 19.0501 |
| 13/16 | 0.8125 | 20.6375 |
| 7/8 | 0.875 | 22.2251 |
| 15/16 | 0.9375 | 23.8125 |
| 1 | 1.00 | 25.4001 |
Temperature Conversions
Most digital thermometers and optical pyrometers read in both Farenheit and Celsius, so we won't present a table here. You can convert temperature units with our handy JavaScript temperature conversion calculator. And here are the conversion formula if you are really Old School and want to use your TI-30 or slide rule:
| Centigrade to Fahrenheit | Fahrenheit to Centigrade |
| (C x 9/5) + 32 = F | (F - 32) x 5/9 = C |
Pressure Conversions
You can convert presure units with our handy JavaScript pressure conversion calculator. Here's a conversion table in case you are allergic to JavaScript:
| mbar | Torr | inches Hg | psi | Pa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mbar | 1 | 0.750 | 0.0295 | 0.0145 | 100 |
| Torr | 1.333 | 1 | 0.0394 | 0.0193 | 133.32 |
| Inches Hg | 33.864 | 25.409 | 1 | 0.491 | 3,386.33 |
| psi | 68.946 | 51.714 | 2.036 | 1 | 6,894.65 |
| Pa | 0.01 | 0.00750 | 0.000295 | 0.000145 | 1 |
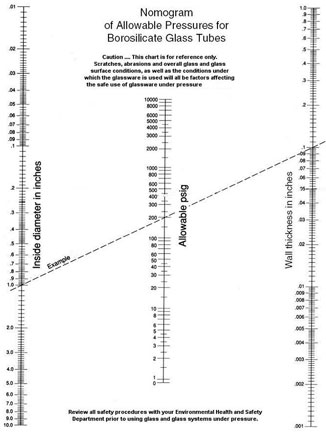
Glass Tubing Pressure Nomogram
Glass can be used under vacuum or pressure, but the larger the pressure differential, the thicker the glass must be. Even so, every time the glassware is used under pressure differentials of more than one atmosphere (760 torr) it must be thoroughly inspected for defects, star cracks and other potential points of failure before pressurization. Safety shields and other forms of protection are also necessary.
This handy nomograph tells the glassblower how thick the wall of a borosilicate glass tube should be in order to withstand a given pressure. One should always build in an extra margin of safety when designing such apparatus:
Physical Properties of Common Glasses
| All temperatures are given in |
Soft Glass (Soda Lime) |
Borosilicate (Duran, Kimax, Pyrex) |
Quartz (Fused Silica) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Softening Range | 696 | 821 | 1580 |
| Working Range | 1000 | 1200 | 1800 |
| Annealing Range | 514 | 565 | 1050 |
| Max Service Temp. | 450 | 490 | 1100 |
The information in this section should be used as a source of comparative figures only, representing a broad range of glasses within their respective family groups. For specific technical data each glass should be identified as to manufacturer and glass code number.
Glass to Metal Sealing Combinations
|
On occasion, a glassblower may be asked to construct a piece made of glass and some other material. For example, a conductivity cell might need an electrode embedded in the glass or a glass high vacuum manifold may need to mate to a metal thermocouple. Making such connections directly is nearly impossible because the two materials have to have very similar thermal coefficients of expansion and other properties. By using a graded seal like the one shown to the right, one can join extremely short lengths of glass that vary from each other by just a little bit and achieve a smooth transition from one material to another. These will span the range between the borosilicate or quartz and the other material. These table below contains some of the most common combinations. |
 |
| Material | Material to Glass Seal |
|---|---|
| Platinum | 7740 (not vacuum tight) |
| Tungsten | 3320 - 7740 |
| Kovar | 7052 - 7720 - 3320 - 7740 |
| Alumina | 7280 - 7056 - 7052 - 3320 - 7740 |
| Tungsten to Quartz Seal | |
| Tungsten 0.30 - 0.40 mil | 7230 sleeve or GE#1 cane - Fused Quartz |
| Numbers refer to Corning code numbers | |
Vacuum Formed 0.500" OD Quartz Tubing
Start with a 0.374" graphite machined rod mandrel and 10 mm ID x 13 mm OD Quartz starting stock
Glass Frit Porosities
 |
Fritted glass is a porus filter made of glass fibers or granules. They are widely used in inorganic and organic laboratories and come in many different forms. Fritted funnels are used for liquid/solid separation and purification. Fritted gas dispersion tubes are used to absorb/remove/dry gases, disperse gases in liquid solutions, and many other applications. They are typically found in disc or cylindrical form in borosilicate and quartz glass. You can learn more about glass fritted funnels and their care in the Glassware Gallery. |
This chart shows the porosity designations and their meanings for glass frit proucts from Ace, Corning, and Kimble:
| Porosity Range Cross Reference Chart (microns) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Common Uses | Ace | Corning | Kimble |
| Gas Dispersion, Coarse Filtration | A 145-174 |
EC 170 - 220 |
EC 170 - 220 |
| Filtration, Gas Dispersion | C 25-50 |
C 40-60 |
C 40-60 |
| Filtration, Extraction | D 10-20 |
M 10-15 |
M 10-15 |
| Filtration, Extraction | E 4-8 |
F 4-5.5 |
F 4-5.5 |
| Bacteria Filtration | VF 2-2.5 |
VF 2-2.5 |
xx |
EC = Extra Coarse, C = Coarse, M = Medium, F = Fine, VF= Very Fine
Glass Properties and Technical Data Sources
- Quartz Properties at Momentive Performance Materials Inc.
- Technical information sheets at Kimble Chase (formerly Kimble-Kontes; now part of Thermo-Fisher) at the Internet Wayback Machine.
- Quartz properties and handling at Tosoh Quartz (scroll down)
- Product information and specifications at Schott Glass.
- Ceramic properties at Mindrum Precision.
- Simax (a division of Kavalierglass offers various types of tubing, capillary and rods.
- Vacuum Gauges - Types And Applications at HighVac Depot.
- GE Quartz Calculators - Internal Stress, Transmission, Window Thickness at Momentive Performance Materials.
- Martindale's Reference Calculators, an extensive calculator database.
General and Miscellaneous Technical Resources
- O-Ring Database at Marco.
- Aremco Products manufactures high temperature glass/ceramic adhesives and coatings
- Modern Vacuum Practice had a list of vacuum links with interesting and handy information such as pump choices, how a thermos works, and more (archived thanks to the Internet Wayback Machine).
- Compressed Gas and Equipment resources at OSHA.
On our General Glassblowing Resources Page you will find books, organizations, tool suppliers, glass suppliers, descriptions of laborator glassware, and art glass links.