



Find all of your laboratory and workplace safety supplies at Safety Emporium!
 Bronchitis |
 Glossary Index |
 Carbon Monoxide |
| MSDS Topics |
Free Sites | FAQ's | Regulations | Glossary | Software | Suppliers |
| Books | Forum | Poll | Fun stuff | Quiz | Store | |
| Understand your MSDS with the MS-Demystifier | Search ALL our MSDS info | |||||

Get your CO2 extinguishers at Safety Emporium
Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless, faintly acidic-tasting, and non-flammable gas at room temperature. Solid carbon dioxide, also known by the trade name Dry Ice, sublimes (converts directly from a solid to a gas) at -78 oC (-109 0F) or above.
Carbon dioxide is a molecular solid with a molecular formula CO2. The linear molecule consists of a carbon atom that is doubly bonded to two oxygen atoms, O=C=O.
Note: Although both are common products of combustion, DO NOT confuse non-toxic carbon dioxide with deadly poisonous carbon monoxide.
Carbon dioxide is the fourth most-abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere. Animals exhale carbon dioxide and plants use photosynthesis to convert it to sugars and other forms of energy.
Commercially, carbon dioxide has thousands of uses. The most familiar example is its use to carbonate soft drinks and beer. It also finds use in a technology called supercritical fluid extraction that is used to decaffeinate coffee. Dry Ice has been used in theatrical productions to make stage fogs (although some modern fog machines now use glycol or glycerin-based solutions instead) and to make "magic potions" bubble as demonstrated on the right.

A common misconception is that carbon dioxide is a visible gas. The white mist that one sees around solid carbon dioxide is actually water vapor that has condensed from the air. The discharge from a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher is white partly due to condensed water vapor and partly due to solid CO2 "snow" which quickly sublimes into invisible carbon dioxide gas.
Carbon dioxide dissolves slightly in water to form a weak acid called carbonic acid, H2CO3:
CO2 + H2O 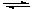 H2CO3
H2CO3
Carbonic acid reacts slightly and reversibly in water to form a hydronium cation, H3O+, and the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-:
H2CO3 + H2O 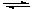 HCO3- + H3O+
HCO3- + H3O+
This chemical behavior explains why water, which normally has a neutral pH of 7 has an acidic pH of approximately 5.5 when it has been exposed to air. It also explains the burning/stinging sensation in your nose and eyes when you inhale too quickly from a freshly-opened container of soda pop; the gas quickly reacts with the water in your eyes and nose to form a small amount of carbonic acid.
The primary health dangers of carbon dioxide are:
Chapter 53 (Compressed Gases) of the 2018 International Fire Code (IFC), Section 5307.3 addresses carbon dioxide systems used in beverage dispensing applications, requiring either ventilation or an emergency alarm system where carbon dioxide is used or can collect. NFPA 55, the Compressed Gases and Cryogenic Fluids Code, also has alarm requirements for CO2 systems (access is free with registration).

Safety Emporium has a great lineup of gas cylinder signs, storage racks, lockouts, clamps and more.
While such pressures are no problem for pressure-tested gas cylinders or fire extinguishers, ordinary containers (soda bottles, paint thinner cans, Thermos containers etc.) can not handle such pressures and will explode and create shrapnel if solid carbon dioxide is sealed inside them. Putting solid carbon dioxide into any sort of closed container (glass, plastic, metal etc.) is exceedingly dangerous and is likely to result in severe personal injury or death.
If, after reading the above paragraphs, you are even thinking about making a carbon dioxide bomb as a "prank", you are a complete idiot. We have personally read the full medical report of a middle school student who lost an eye in 2006 - to one of several bombs deliberately built by his teacher as a "demonstration". And in 2011, A Chicago-area teacher took out his student's eye attempting to demonstrate pressure by sealing solid carbon dioxide in a plastic bottle. Not only is the risk of injury (or even death) very high, in many states constructing, possessing or using such a device is a felony. See Salt Lake Police Department's Bomb Squad warns against homemade chemical bombs.
Finally, note that carbon dioxide is a "greenhouse gas". Although it is naturally present in the atmosphere, Man's activities such as the combustion of fossil fuels have drastically increased the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere and contributed to global warming.

All rooms with fixed extinguishing systems must have appropriate warning signs like this one from Safety Emporium.
You are most likely to encounter carbon dioxide on a Safety Data Sheet in reference to in Section 5 (fire-fighting measures). Carbon dioxide extinguishers are not appropriate for all fires, especially those involving flammable metals and pyrophoric substances. Using a CO2 extinguisher on such fires would be very much like putting gasoline on a fire! For more information about fire extinguishers and a downloadable PowerPoint presentation, visit our Fire Extinguishers page.
If your company uses an automatic fire extinguishing system (such as in a computer room or where flammable organic solvents are used), critical precautions must be taken to avoid asphyxiation. Special signage and training is essential. Three different OSHA standards cover fixed fire extinguishing systems; see the OSHA link under Further Reading below.
You may also find carbon dioxide mentioned as a decomposition product or as an incompatible material in Section 10 (stability and reactivity) of the SDS.

Supply of laboratory gases is a snap with laboratory ball valves from Safety Emporium.
See also: Asphyxiation, organic, vapor.
Additional definitions from Google and OneLook.